Let’s talk about phobias
Lesson 1

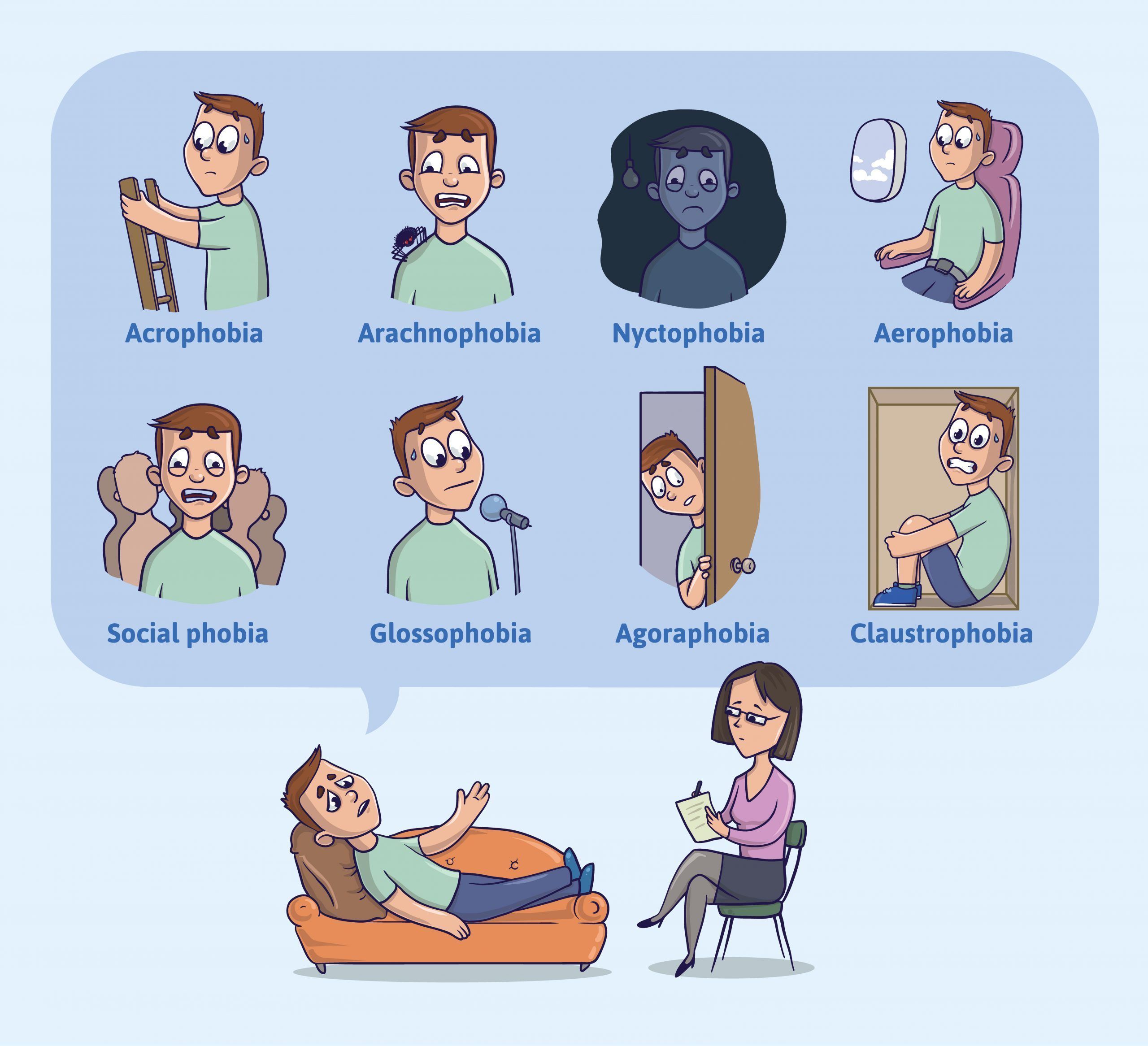
WHAT ARE YOU SCARED OF
Spiders, birds, mice, or even Clowns - most people get the heebie-jeebies about something.
Nevertheless, there are times when this worry becomes an intense, irrational fear when they face a certain situation, activity, or object and it is called a phobia.
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders reported that 30% of those suffering from a specific phobia will only seek treatment.
It can stop people trying things they would like to do. In some situations, it also can prevent them from functioning normally and may lead to a panic attack..
The word comes from the Greek term, phobos,
and it refers to a severe and irrational dislike of an object, place, situation, feeling or animal. People with a phobia have an overpowering need to avoid anything that triggers their anxiety. And it refers to a severe and irrational dislike of an object, place, situation, feeling or animal. People with a phobia have an overpowering need to avoid anything that triggers their anxiety.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder( GAD)
Is different from say having a phobia. People with phobias are fearful of something in particular – for example, spiders, heights, or speaking in public. If you have GAD, you have an uneasy feeling about life in general. It’s often associated with feelings of dread or unease and you’re in a state of constant worry over everything. For example, if a friend doesn’t call you back within an hour, you may start to worry you did something wrong and the friend is upset with you.
The term 'phobia' is often used to refer to a fear of one particular trigger. However, there are three types of phobia recognized by the American Psychiatric Association (APA).
These include:
Specific Phobia:
This is an intense, irrational fear of a specific trigger.
Specific phobias are known as simple phobias as they can be linked to an identifiable cause that may not frequently occur in the everyday life of an individual, such as snakes. These are therefore not likely to affect day-to-day living in a significant way.
Complex Phobia:
These are linked to a particular situation or circumstance. The two most common types are:
Agoraphobia:
The fear of being in situations where escape might be difficult or help wouldn't be available if things went wrong.
Social Phobia:
Which can be an overwhelming fear of social situations.
specific phobia
The most common type of specific phobia is zoophobia or fear of animals. Zoophobia is actually a generic term that encompasses a group of phobias involving specific animals.
Examples include:
- arachnophobia -- fear of spiders
- ophidiophobia -- fear of snakes
- ornithophobia -- fear of birds
- apiphobia -- fear of bees.
Such phobias often develop in childhood and sometimes go away as the child ages.
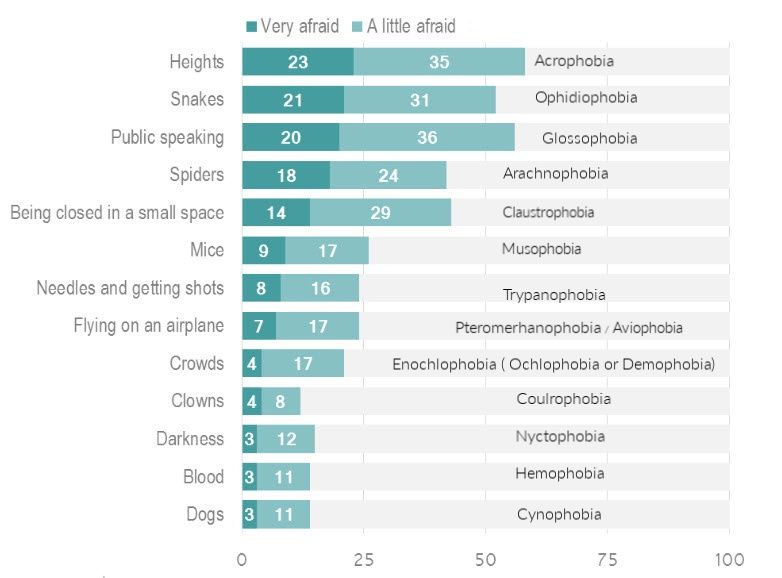
Some 23 per cent of the UK population is very afraid of being up high, with another 35 per cent a little afraid. This is Acrophobia, It belongs to a category of specific phobias, called space and motion discomfort and is an excessive fear of heights. It doesn't just mean standing on top of a tall building either - it covers anything that is off the ground, even going on escalators.
A person could have an attack just walking up stairs or climbing a ladder. Sometimes the fear is so great a person can't move. Acrophobia can create a dangerous situation for someone who has it. An anxiety attack can make it extremely difficult to safely get down from whatever high place triggered the attack.
When it comes to the animal kingdom, snakes hold the biggest fear for Brits - some 52 per cent have
ophidiophobia.

They may be called 'man's best friend, but dogs make life very difficult for the 14 per cent of the population who have cynophobia.
Although snakes and spiders are more common animal phobias, cynophobia is especially debilitating because of the high prevalence of dogs world wide with an estimated 62 million pet dogs in the United States and the general ignorance of dog owners to the phobia.
People with complex phobias will use a classic avoidance behaviour to avoid triggers, such as not leaving the house or being in a large crowd. In the case of cynophobia, staying away from areas where dogs might be (eg, a park), crossing the street to avoid a dog, or avoiding the homes of friends or family who own a dog.
Spiders scare 33 per cent of men compared to 52 per cent of women. Figures from yougov.co.uk
With a phobia, you may know your anxiety and fear are not warranted, but you can't help the feelings. They can be so intense they virtually paralyse you.
Blood Injury
There is a spectrum of blood, injection, and injury phobias including hemophobia (fear of blood) and trypanophobia (fear of receiving an injection).
Some people have an injury phobia, and others have a phobia about invasive medical procedures. These phobias are associated with fainting.
An estimated 19 million Americans have a phobia that causes difficulty in some area of their lives.
If you have a phobia that's affecting your life, don't feel you have to try to deal with it alone.
Many counsellors are experts in techniques for overcoming and understanding phobias.
Talk to a trusted person about it.
Arachnophobia:
Means fear of spiders. If you have this, you will know that even the thought of one of those eight-legged arthropods can bring you out in a hot rash while seeing one in a picture (let alone in the flesh) can turn you into a babbling nervous wreck.
Imagine having a fear of flying (aviophobia or aerophobia) and arachnophobia (spiders) - Australia would be a non-starter.
However, these are just two of the many thousands of phobias out there and below is a list of other phobias:

- e - I
- K - N
- O - T
- V - Z
- Achluophobia - Fear of darkness
- Acrophobia - Fear of heights
- Agoraphobia - Fear of being in a situation where escape might be difficult or that help wouldn't be available.
- Aerophobia - Fear of flying
- Algophobia - Fear of pain
- Agoraphobia - Fear of open spaces or crowds
- Aichmophobia - Fear of needles or pointed objects
- Ailurophobia - Fear of cats
- Amaxophobia - Fear of riding in a car
- Androphobia - Fear of men
- Anginophobia - Fear of angina or choking
- Anthrophobia - Fear of flowers
- Anthropophobia - Fear of people or society
- Aphenphosmphobia - Fear of being touched
- Arachibutyrophobia - Fear of peanut butter
- Arachnophobia - Fear of spiders
- Arithmophobia - Fear of numbers
- Astraphobia - Fear of thunder and lightning
- Ataxophobia - Fear of disorder or untidiness
- Atelophobia - Fear of imperfection
- Atychiphobia - Fear of failure
- Automatonophobia - Fear of Human-Like Figures
- Autophobia - Fear of being alone
- Bacteriophobia - Fear of bacteria
- Barophobia - Fear of gravity
- Basiphobia - Fear of walking
- Bathmophobia - Fear of stairs or steep slopes
- Batrachophobia - Fear of amphibians
- Belonephobia - Fear of pins and needles
- Bibliophobia - Fear of books
- Botanophobia - Fear of plants
- Brontophobia - Fear of thunder.
- Cacophobia - Fear of ugliness
- carcinophobia or cancerophobia - Fear of developing cancer.
- Catagelophobia - Fear of being ridiculed
- Catoptrophobia - Fear of mirrors
- Chionophobia - Fear of snow
- Chiroptophobia - Fear of bats (vampires)
- Chromophobia - Fear of colours
- Chronomentrophobia - Fear of clocks
- Chronophobia - Fear of Time
- Claustrophobia - Fear of confined / small spaces
- Coulrophobia - Fear of clowns
- Cyberphobia - Fear of computers
- Cynophobia - Fear of dogs
- Dendrophobia - Fear of trees
- Dentophobia - Fear of dentists
- Domatophobia - Fear of houses
- Dromophobia - Fear of crossing streets
- Dystychiphobia - Fear of accidents
Entomophobia:
Is the fear of doors and a debilitating phobia often associated with Agoraphobia and Claustrophobia.

In sufferers with the general fear of doors, there may be the general tendency of being afraid of the insecurity or fear of the unknown that lies outside.
Hypnotherapy is another well-known treatment option for this phobia which can help change the construct of the phobias mind to help him/her deal with the anxiety that triggers the fear of doors.
Gradual desensitization therapy could also help in many cases; here, the phobics learn to gradually expose themselves to doors-both open and shut- until they are able to deal with their Entomophobia in their daily lives.
Amaxophobia:
The fear of being a passenger, can be virtually crippling. Imagine how life-limiting it would be if you were too afraid to be a passenger in a car, bus, train, or airplane.
Thankfully, many, though not all, people with amaxophobia can drive their own cars.
The prospect of allowing someone else to take control of the trip, however, is terrifying for them..

Complex Phobia - Agoraphobia
The agora was a market and meeting place in ancient Greece. Someone with agoraphobia is afraid of being trapped in a public place or a place like a bridge or a line at the bank. The actual fear is of not being able to escape if anxiety gets too high.
Agoraphobia affects twice as many women as men. If left untreated in extreme cases, it can lead to someone becoming housebound.
Social Phobia
Someone with a social phobia is not just shy. That person feels extreme anxiety and fear about how he or she will perform in a social situation. Will her actions seem appropriate to others?
Because untreated social phobia often leads to avoiding social contact, it can have a major negative impact on a person's relationships and professional life.

The burden of a phobia
Phobias cause people to change how they live in order to avoid the object of their fear. Nevertheless, their life is also affected by their attempts to conceal the phobia from others.
Some people with phobias have problems with friends and family, fail in school, or lose jobs while struggling to cope.
Phobias and Alcohol
Alcoholics can be up to ten times more likely to suffer from a phobia than those who are not alcoholics.
Genetic
Although phobias can be influenced by culture and triggered by life events, they tend to run in families. Immediate family members of people with phobias are about three times more likely to have a phobia than those without a family history.
Treatment

Systematic desensitisation therapy was introduced by Joseph Wolpe in 1958 and employs relaxation techniques with imagined situations. Desensitisation is a process of gradually exposing someone with a phobia to circumstances that resemble what he fears.
Over time, the fear lessens as the person builds confidence. This is often accompanied by cognitive therapy (talking therapy) to help the person change how s/he thinks and develop new patterns of response to situations that might trigger the emotions associated with a phobia.
The good news is treatment helps 90% of people who follow through.

Mindfulness based cognitive therapy (MBCT) has been shown to help individuals with a phobia to reduce their symptoms and overcome their phobia.
Medication
Medication isn't usually recommended for treating phobias, because talking therapies are usually effective and don't have any side effects. However, medication is sometimes prescribed on a short-term basis to treat the effects of phobias, such as anxiety.
There are 3 types of medication recommended for treating anxiety:
- antidepressants
- tranquillisers
- beta-blockers
Antidepressants
Antidepressants are often prescribed to help reduce anxiety. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are most often prescribed to treat anxiety, social phobia or panic disorder.
These can include:
- escitalopram (Cipralex)
- sertraline (Lustral)
- paroxetine (Seroxat)
Venlafaxine (Efexor), a serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) may also be prescribed for anxiety.
Common side effects of these treatments include:
- nausea
- headaches
- sleep problems
- upset stomach
They may also, initially, make your anxiety worse and can cause sexual problems.
Clomipramine (Anafranil) is a type of tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that's licensed to treat phobias.
Side effects include:
- dry mouth
- drowsiness
- blurred vision
- tremors (shaking)
- palpitations (irregular heartbeat)
- constipation
- difficulty urinating
Moclobemide (Manerix) is a type of antidepressant from the monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) group of antidepressants. It's sometimes prescribed to treat social phobia.
Moclobemide interacts with certain types of food, so if you're prescribed this medication, read the information leaflet that comes with it to find out which foods to avoid.
Other possible side effects of moclobemide include:
- sleep problems
- dizziness
- stomach problems
- headaches
- restlessness
- agitation
If you're prescribed antidepressants, it's very important that you don't suddenly stop taking them. Suddenly stopping can cause withdrawal symptoms.
See your GP, who can gradually lower your dose.
Tranquillisers
Benzodiazepines are a group of medicines that are categorised as minor tranquillisers. They include medicines such as diazepam (Valium) and are sometimes used on a short-term basis at the lowest possible dose to treat severe anxiety.
Like antidepressants, benzodiazepines should be stopped gradually to avoid withdrawal symptoms.
Beta-blockers
Beta-blockers are often used to treat cardiovascular conditions, such as heart problems and high blood pressure (hypertension). They are also sometimes prescribed to help reduce the symptoms of anxiety, such as palpitations (irregular heartbeat).
Beta-blockers slow down your heart rate and decrease your blood pressure.
Propranolol (Inderal) is a beta-blocker that's commonly used to treat anxiety.
Possible side effects include:
- stomach problems
- cold fingers
- tiredness
- sleep problems
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/phobias/treatment/
Further reading
https://www.drugwatch.com/health/how-to-deal-with-anxiety/
https://www.drugwatch.com/health/mental-illness/
https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/generalised-anxiety-disorder/
https://adaa.org/about-adaa/press-room/facts-statistics
https://yougov.co.uk/
https://yougov.co.uk/topics/politics/articles-reports/2014/03/20/afraid-heights-not-alone
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Diagnostic_and_Statistical_Manual_of_Mental_Disorders
https://addictionrehabtreatment.com/mental-health/phobias/chronic-phobias/
Chronic Phobias: Types, Symptoms and Treatment
Chronic Phobias include the chronic fear of flying, claustrophobia, and complex phobias like social phobia and agoraphobia. Learn more about chronic phobias and how to treat them.
The following book reviews contain a mental health study on personality disorder.
Intellectual humility is the recognition that our own beliefs and perspectives may
Which therapy offers the best value for an anxious patient using either,
Today's articles look at the darker side of love with abuse, which
Our previous session discussed how literature and the media manipulated public opinion