- in Emotional distress , Relationships by Tony
Unlocking the Enigma: Understanding Alexithymia and its Impact on Emotional Well-being.

In our quest to unravel the complex workings of the human mind, we often encounter enigmatic conditions that confound our understanding.
One such condition is Alexithymia, also known as (AKA) emotional blindness. This fascinating yet little-known phenomenon profoundly affects one’s emotional well-being.
More...
Unlocking the secrets of this mysterious condition is essential for gaining insight into the intricate mechanisms underlying our emotions and paving the way towards improved psychological health.
In this article, we delve into the depths of Alexithymia, examining its definition, symptoms, and profound impact on someone’s ability to navigate the intricacies of their emotional landscape.
Join us as we embark on a journey of exploration and discovery, aiming to shed light on this perplexing psychological trait and its implications for emotional well-being.
The Origins and Definition of Alexithymia: We Hold the Key to Unravelling this Enigma.

Peter Emanuel Sifneos introduced into psychiatry the term alexithymia, published in 1972 was then viewed as a deficit in emotional awareness, but it also had origins in Freudian psychodynamic literature.
According to research, alexithymia is more common in males, with approximately 8% of men experiencing it compared to 2% of women. However, it is necessary to note that these numbers may not accurately reflect the true prevalence, as alexithymia often goes undiagnosed or unrecognised.
Studies have also suggested the possibility of cross-cultural differences in alexithymia and found to be more elevated within rural areas relative to urban populations.
In our relentless pursuit to understand the complexities of the human mind, we are often confronted with perplexing conditions that defy explanation. One such condition is Alexithymia, a captivating yet relatively unfamiliar phenomenon that profoundly impacts an individual’s emotional well-being.
To unlock the enigmatic nature of this condition is vital, as it provides us with invaluable insight into the intricate mechanisms that govern our emotions, leading to potential advancements in psychological health. This article now delves more into Alexithymia’s depths, definition, symptoms, and far-reaching consequences on individuals.
At its core, Alexithymia is characterised by an individual’s difficulty recognising, processing, and expressing emotions.
The word itself stems from the Greek words “a-lexis” meaning “lack of words” and “thymos” meaning “emotion” or “soul.”
This roughly denotes “no words for emotion.” Thereby, individuals with Alexithymia struggle to find the appropriate words to describe their internal emotional experiences, often leading to a sense of detachment and disconnection from their own particular feelings. The deficiency in emotional awareness can manifest in various ways, such as an inability to differentiate between physical sensations and emotions or a tendency to rely on external stimuli to understand their emotional state.
Such blunted emotional awareness can range from mild to severe, and is often associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Regarding comorbidity, alexithymia is commonly associated with conditions such as depression, anxiety, trauma, schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) and substance misuse, to name a few psychological disturbances.
It is important to note that alexithymia is not a mental illness, but a personality trait or characteristic that individuals may possess. However, it can contribute to mental health challenges and should be addressed and treated as part of an individual’s overall well-being.
Relationships

The consequences of Alexithymia are far-reaching, impacting an individual’s emotional well-being, relationships, and overall quality of life. The inability to effectively communicate and understand one’s emotions can hinder the development of meaningful connections with others, leading to difficulties in forming and maintaining intimate relationships.
Similarly, the lack of emotional intimacy and depth in relationships affected by Alexithymia can hinder bonding and intimacy. Emotional connection is a vital aspect of any healthy relationship. When one or both partners struggle with identifying and expressing emotions, it can create a barrier that prevents true intimacy from being established.
Moreover, individuals with Alexithymia may experience heightened levels of psychological distress as they struggle to navigate through their own emotional landscapes, often feeling overwhelmed and unable to find a resolution. By unravelling the enigma of Alexithymia, we can empower individuals with this condition to better understand themselves, seek appropriate support, and ultimately improve their emotional well-being.
Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria: How to Identify Alexithymia
Symptoms and diagnostic criteria are crucial in identifying Alexithymia, a complex emotional well-being condition. Individuals with Alexithymia often struggle to identify and describe their own emotions, making it challenging to understand and connect with their feelings.
This difficulty in recognising and expressing emotions is a distinctive characteristic of Alexithymia. One of the primary symptoms of Alexithymia is an inability to differentiate between physical sensations and emotional experiences. These individuals may struggle to pinpoint specific emotions and tend to describe their feelings in terms of physical sensations, such as stomachaches or headaches, rather than emotional ones.
Additionally, those with Alexithymia may find it challenging to relate to and empathise with others, lacking the ability to understand and interpret social cues related to emotions.
Diagnostic tool

To diagnose Alexithymia, mental health professionals utilise specific diagnostic criteria. The Toronto Alexithymia Scale (TAS-20) is a commonly used assessment tool that measures various facets of Alexithymia, and they may have an ordeal describing emotions and externally oriented thinking.
Through a comprehensive evaluation of these symptoms and criteria, individuals can be accurately identified as having Alexithymia, allowing for appropriate interventions and support to enhance their emotional well-being.
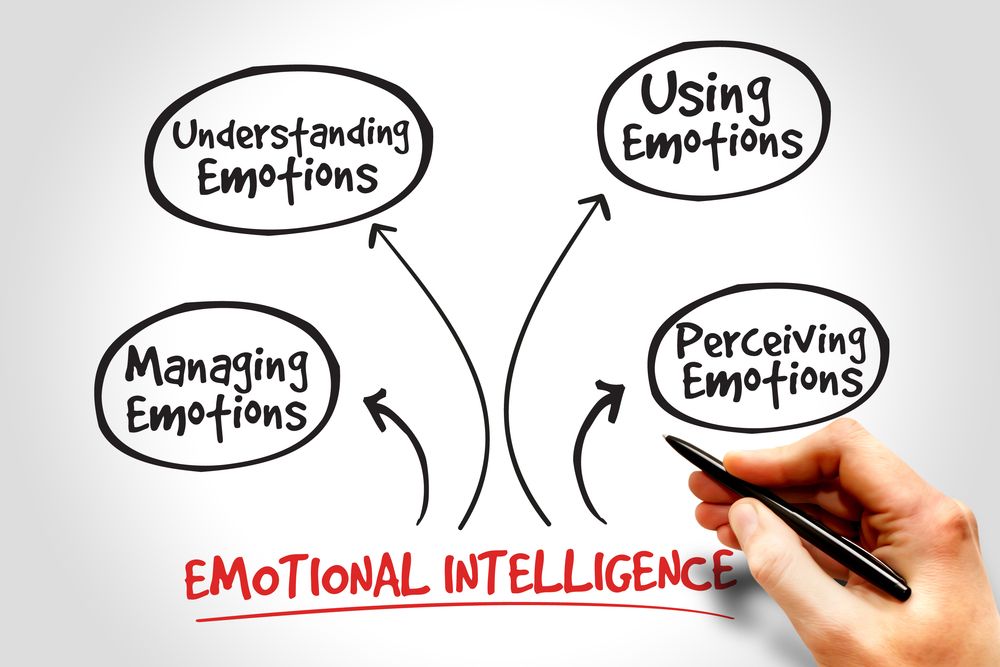
The Impact of Alexithymia on Emotional Intelligence and Communication Skills
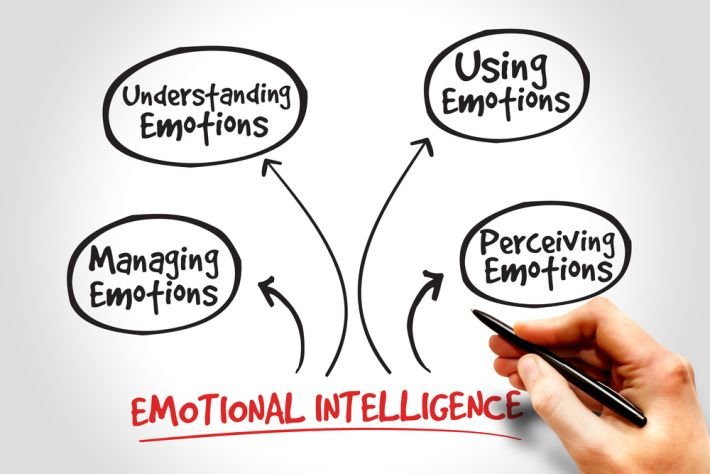
The impact of Alexithymia on emotional intelligence and communication skills cannot be understated. Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognise, understand, and manage one’s own emotions as well as the emotions of others.
In this case, Alexithymia is characterised by difficulty identifying, understanding, and expressing one’s emotions, indicating a deficit in empathy within the framework of the self. It appears we have to declare an impasse in this situation.
However, it is important to note that emotional intelligence is a broad concept that encompasses various components, such as emotional awareness, emotional regulation, and social skills. While individuals with alexithymia may face difficulties in certain aspects of emotional intelligence, they may still possess strengths in other areas.
It is possible for someone with alexithymia to develop their emotional intelligence through self-reflection, therapy, or other forms of support. With guidance and practice, they can learn to improve their emotional awareness, enhance their understanding of emotions, and develop strategies to regulate and express their own emotions effectively.
Although it may require more effort and assistance, individuals with alexithymia can work towards developing a reasonable level of emotional intelligence.
One influential aspect of the framework is self-awareness, which refers to the ability to recognise and understand one’s own feelings. It involves being mindful and attentive to one’s internal emotional states, and being able to label and differentiate between various emotions.
Just consider for a moment, if someone employs simulation theory to predict their understanding of the feelings of others but then lacks the capacity to interpret and describe their own emotions accurately, they will struggle to empathise or appreciate the emotions of others.
This inability to accurately recognise, and articulate emotions can severely hinder an individual’s emotional intelligence, which requires understanding and managing one’s emotions to empathise with others intellectually in relationships and business.
People with Alexithymia struggle to communicate effectively, as emotions are crucial in expressing oneself and understanding others. Their limited emotional vocabulary and lack of interoceptive emotional awareness, a critical aspect of empathy, making it difficult for them to accurately convey their thoughts and feelings, leading to misunderstandings and ineffective interpersonal relationships.
Additionally, individuals with Alexithymia may have difficulty recognising non-verbal cues and body language, further impeding their communication ability.
Furthermore, Alexithymia profoundly impacts emotional intelligence, which is essential for navigating various social situations. Emotional intelligence encompasses skills such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and social awareness.
Whereas, individuals with alexithymia may struggle with empathy and have difficulty emotionally understanding and connecting with others.
By impairing an individual’s ability to recognise and understand their own emotions, Alexithymia hinders their self-awareness, making it challenging to regulate their own emotions effectively.
Is Emotional Intelligence and Social Intelligence the same concept
No, emotional intelligence and social intelligence are not the same concept, although they are related. In his book, Mastery, Robert Greene defines social intelligence as “the ability to see people in the most realistic light possible”.
Whereas, Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to identify, understand, and manage one's own emotions, as well as recognising and empathising with the emotions of others. It involves skills such as self-awareness, self-regulation, empathy, and interpersonal relationships.
On the other hand, social intelligence refers to the ability to navigate and understand social situations effectively. It includes skills such as reading social cues, understanding social norms and expectations, and adapting one's behaviour accordingly. Social intelligence encompasses a broader range of social skills beyond just emotions.
While emotional intelligence is certainly a part of social intelligence, the latter also includes other aspects such as understanding social dynamics, influencing others, and communication skills. Both emotional and social intelligence are important for successful social interactions, but they are distinct concepts with some overlap.
To summarise, Alexithymia significantly affects emotional intelligence and communication skills. Understanding this enigmatic condition is essential for developing strategies and interventions that can aid individuals in managing their feelings and improving their overall emotional well-being.
By recognising and addressing Alexithymia, individuals can embark on a journey towards enhanced emotional intelligence and healthier interpersonal relationships.
Understanding the Neurobiology of Alexithymia: Insights from Research
Understanding the neurobiology of Alexithymia is crucial for gaining insights into this enigmatic condition and its impact on emotional well-being. Alexithymia is a complex phenomenon characterised by difficulties in recognising, expressing, and describing one’s emotions.
Research suggests that alexithymia may be linked to various underlying causes, including genetic factors, childhood trauma, and neurological differences in brain structure and function.
Individuals with Alexithymia tend to have reduced connectivity between the brain’s cognitive and emotional centres, leading to emotional processing and regulation challenges. Neuroimaging studies have revealed structural and functional differences in the brains of individuals with Alexithymia compared to those without the condition. These differences often involve areas such as the prefrontal cortex, insula, and amygdala, which play crucial roles in emotion regulation and awareness.
Dysfunction in these regions can result in a limited ability to perceive and understand one’s emotions, leading to difficulties in forming meaningful emotional connections with others. Insights from research have also highlighted the negative impact that Alexithymia has on emotional well-being.
Individuals with Alexithymia often experience higher levels of psychological distress, difficulty managing stress, and reduced overall life satisfaction. Understanding the neurobiology of Alexithymia provides valuable knowledge about this perplexing condition and opens up potential avenues for developing effective interventions to improve the emotional well-being of affected individuals.
The Link Between Alexithymia and Mental Health Disorders: Exploring Comorbidity

Understanding Alexithymia and its Impact on Emotional Well-being delves into the link between alexithymia and mental health disorders, specifically exploring the concept of comorbidity. It is important to note that alexithymia is not a widely recognised or understood condition, which can lead to misunderstandings and stigmatisation.
By unravelling the enigma of alexithymia, researchers aim to understand better the intricate mechanisms that underlie our emotions and ultimately contribute to improved psychological health.
By examining the definition and symptoms of alexithymia, this article sheds light on how this condition affects an individual’s emotional well-being. Alexithymia is characterised by difficulties in identifying and expressing emotions, and those who experience it often have limited awareness of their own emotions.
Individuals with alexithymia may also have difficulties in regulating their emotions. They may struggle to find appropriate ways to cope with intense feelings, often resorting to maladaptive behaviours such as excessive substance use or emotional detachment.
Additionally, the lack of emotional insight can lead to increased distress and ineffective coping mechanisms. Therefore, it is crucial for healthcare professionals to recognise the potential comorbidity between alexithymia and mental health disorders when assessing patients.
The impact of alexithymia on mental health disorders is another crucial aspect discussed in the article. Through exploring the concept of comorbidity, researchers have found that alexithymia is commonly associated with conditions such as anxiety, depression, eating disorders, and substance abuse.
Understanding the link between alexithymia and these mental health disorders is essential for developing effective treatment strategies and improving the emotional well-being and overall quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
The connection between childhood maltreatment and alexithymia is thought to be rooted in the disruption of emotional processing and regulation resulting from trauma.
When children are exposed to adverse experiences, their ability to recognise and express emotions can become compromised. This can lead to difficulties in forming healthy attachments, regulating emotions, and understanding the emotions of others.
Furthermore, the effects of childhood maltreatment can extend beyond the individual’s emotional well-being. Studies have shown that individuals with a history of trauma-related alexithymia may also be at an increased risk for various mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, and substance abuse.
Coping Strategies and Treatment Approaches for Individuals with Alexithymia

A multimodal approach that combines counselling or therapy with medication management, if needed, can provide comprehensive support for individuals with alexithymia. By addressing the root causes of alexithymia and equipping individuals with tools to understand and regulate their emotions, treatment approaches can empower them to lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
Applying varies coping strategies and treatment approaches are crucial in assisting individuals with alexithymia to manage their emotional well-being. Due to the nature of this condition, characterised by difficulties in identifying and expressing emotions, individuals with alexithymia may benefit from learning strategies to help them navigate their emotions more effectively.
One such approach is psychotherapy, where therapists can provide a safe and supportive environment for individuals to explore their emotions and develop skills to recognise better and express them. Although there is no specific cure for alexithymia, therapy approaches such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) can help individuals develop skills for recognising and expressing their emotions more effectively.
Cognitive-behavioural therapy focuses on changing negative patterns of thinking and behaviour by challenging irrational thoughts and beliefs. In the context of alexithymia, cognitive-behavioural therapy can help individuals become more aware of their emotions by identifying triggers, learning to cope mechanisms, and practising effective communication skills.
Group therapy is another valuable treatment option for individuals with alexithymia. Being part of a supportive group allows individuals to share their experiences, learn from others, and practice emotional expression in a safe environment. Group therapy can provide a sense of belonging and validation, fostering emotional growth and improving overall well-being.
Another treatment approach for individuals with alexithymia is the use of mindfulness-based techniques. Mindfulness focuses on enhancing self-awareness and experiencing emotions in the present moment without judgment. This approach can help individuals with alexithymia develop a greater understanding of their emotions and learn to respond to them in a more adaptive manner.
By practising mindfulness, individuals can develop the skills to observe and acknowledge their emotions, even if they struggle to fully understand or express them verbally.
Furthermore, support groups can provide individuals with alexithymia a sense of belonging and understanding. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can help alleviate feelings of isolation and provide a supportive environment for individuals to discuss their emotions and coping strategies.
These groups can offer a platform for individuals to learn from each other’s experiences and gain valuable insights into managing alexithymia effectively.
It is important to note that treatment for alexithymia may be a long-term process, requiring persistence and commitment from both the individual and the mental health professional.
Progress may be gradual, but with consistent effort and support, individuals can develop emotional insight, improve interpersonal relationships, and experience greater overall life satisfaction.
The deduction from this section, is that coping strategies and treatment approaches, such as psychotherapy, cognitive-behavioural therapy, mindfulness-based techniques, and support groups, are essential for individuals with alexithymia to enhance their emotional well-being.
These approaches can assist in developing emotional awareness, expression, and regulation skills, ultimately leading to improved psychological health and a better quality of life for individuals with alexithymia.
In conclusion, unlocking the enigma of alexithymia is crucial for improving the emotional well-being of affected individuals. By increasing understanding and providing appropriate support and treatment options, we can help those with alexithymia navigate their emotional world more effectively and lead fulfilling lives.