- in Relationships by Tony
- |
- 1 comments
Obsessive Love

Obsessive love can be described as an intense and overwhelming feeling of love towards someone, which can lead to controlling behaviour and possessiveness. It often involves an unhealthy attachment to the other person and can have negative consequences for both the lover and the loved one.
More...
Idolatry, infatuation, and erotomania are terms used to describe different types of intense feelings or obsessions towards someone or something.
Here’s a brief explanation of each:
1. Idolatry: Idolatry refers to the worship or excessive admiration of an idol or deity. It is often associated with religious or spiritual beliefs and involves the belief that the idol or deity is sacred and deserving of devotion. In this context, idolatry can include rituals, prayers, or offering sacrifices to the idol or deity.
2. Infatuation: Infatuation is an intense and often short-lived passion or attraction towards someone or something. Intense and overwhelming feelings of affection, desire, or fascination characterise it. Infatuation can be based on physical appearance, superficial qualities, or idealized perceptions of the person or object of infatuation. It is typically not rooted in deep emotional connection or long-term commitment.
3. Erotomania: Erotomania is a rare psychological disorder characterised by an individual’s delusion of another person, often of higher social status, being deeply in love with them. Individuals experiencing erotomania firmly believe that their love interest is reciprocating their feelings, despite little or no evidence. This condition is also known as De Clerambault’s syndrome and can lead to obsessive thoughts, stalking behaviours, or even harassment of the perceived love interest.
In summary, idolatry relates to worship or excessive admiration of a sacred object or deity; infatuation refers to intense but often short-lived passion or attraction towards someone or something, and erotomania is a delusional belief that another person is deeply in love with the individual experiencing the condition.
The Dark Side of Love: of an Obsessive Love Disorder (OLD)

Obsessive Love Disorder (OLD) may seem like an innocent infatuation initially, but its dark and complicated nature reveals itself over time.
Exploring the psychological aspects, behavioural patterns, and potential consequences associated with Obsessive Love, we aim to shed light on a topic often veiled by societal stigma.
Join us as we uncover the intricate layers of an obsessive love disorder in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of its far-reaching impact on both sufferers and those entangled in their emotional vehemence.
Individuals afflicted with Obsessive Love Disorder grapple with intense emotional turmoil. Their overwhelming and all-consuming passion for someone can bring about a multitude of psychological challenges.
A Never-Ending Loop of Intrusive Thoughts
Obsessive love fills the mind with repetitive, intrusive thoughts - an incessant reel that plays on loop.
Preoccupied by fantasies and longing, those suffering from this disorder find it difficult to focus on anything or anyone else but their desired object of affection.
This persistent rumination creates a constant state of distress and anxiety, trapping them in a perpetual cycle they are unable to escape from.
Stalking as a Twisted Expression of Love

In some cases, obsessive lovers resort to stalking as a distorted means to express their affections.
Fuelled by an irrational belief that monitoring every move of their beloved will bring them closer together, or bring them answers, and then engage in covert surveillance or online tracking.
This behaviour further deepens their inner torment as it is driven by desperation, paranoia, and an insatiable desire for control.
From Infatuation to Destruction: Unravelling the Behavioural Patterns of Obsessive Love Disorder

Obsessive love disorder is a complex condition characterised by intense infatuation and possessiveness towards a romantic partner.
Individuals often exhibit patterns of behaviour that can be categorised into three main phases: infatuation, fixation and destruction.
- Infatuation: At the initial stage, individuals with OLD experience an overwhelming attraction to their partner, bordering on obsession. They idealize their loved one, seeing them as perfect and placing them on a pedestal above all others. This infatuation consumes their thoughts and emotions, leading to excessive longing for reciprocation.
- Fixation: As the relationship progresses, those with obsessive love disorder become fixated on maintaining control over their partner's actions. This fixation often manifests in possessiveness and jealousy. Their need for constant reassurance leads to monitoring their partner's activities relentlessly, while experiencing extreme anxiety when faced with potential threats or perceived betrayals.
- Destruction: The final phase of an obsessive love disorder is marked by destructive behaviour fuelled by fear of abandonment or rejection. Individuals may resort to manipulation tactics such as emotional blackmail or even stalking out of desperation to keep the relationship intact. In extreme cases, this disorder can escalate into physical violence or domestic abuse.
Understanding these behavioural patterns is crucial in identifying and addressing obsessive love disorder early on before it escalates further into dangerous territory.
Obsessive Love: Understanding the Fine Line Between Passion and Possession

In the realm of love and relationships, emotions can often become entangled in a web of complexities. One such intricate and perplexing phenomenon is obsessive love – an intense passion that blurs the line between affection and possession.
The Origins of Obsessive Love: Exploring the Psychological Factors

Obsessive love can stem from a variety of psychological factors that contribute to its development and intensity. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Attachment Theory: Individuals with insecure attachment styles, such as anxious-preoccupied or fearful-avoidant, may be more prone to developing obsessive love. These individuals often have deep-seated fears of abandonment and seek constant reassurance and validation from their partner.
- Low Self-Esteem: Individuals with low self-esteem may become obsessed with their partners because they see them as the sole source of their self-worth. They rely heavily on the relationship to validate their own existence, leading to an intense fear of losing their partner's affection.
- Past Trauma: Experiences such as childhood neglect, abuse, or past failed relationships can also contribute to the development of obsessive love. Cycles of rejection or betrayal can create unresolved emotional wounds that manifest in intense possessiveness and controlling behaviours.
- Insecurity: Insecure individuals often struggle with feelings of inadequacy or a fear that they are not "good enough." This insecurity drives them to excessively monitor their partner's actions and constantly seek assurance, resulting in possessive behaviour characteristic of obsessive love.
Understanding these psychological factors behind obsessive love is crucial in recognising its complexities and potential dangers it poses for both individuals involved in the relationship.

In psychoanalysis, the focus is on exploring the unconscious conflicts and unresolved childhood experiences that may contribute to the development of obsessive love.
This approach recognises that obsessive love may stem from deep-rooted psychological issues, such as attachment trauma, unresolved feelings of loss or abandonment, or unresolved conflicts with past relationships.
The Origins of Obsessive Love: Exploring the Factors that Contribute to its Development

Factors Contributing to the Development of Obsessive Love
Obsessive love can stem from a variety of factors, each playing a crucial role in its development. Understanding these factors is key to comprehending the complexities underlying this intense emotion:
- Attachment Styles: An individual's attachment style, which is formed during early childhood experiences with caregivers, greatly influences their capacity for healthy relationships. Those with anxious or ambivalent attachment styles tend to be more prone to obsessive love due to their fear of abandonment and intense need for reassurance.
- Low Self-Esteem: Individuals struggling with low self-esteem may seek validation and affirmation from others, leading them into an unhealthy cycle of obsessively pursuing affection and attention. This constant need for approval can drive them towards possessiveness and controlling behaviours.
- Unmet Emotional Needs: Unresolved emotional needs from experiences can contribute to the development of obsessive love. Trauma, neglect, or unresolved conflicts within family or previous relationships may create a void that individuals strive to fill by fixating on one person as their sole source of fulfilment.
- Societal Influences: Society often romanticizes passionate love stories, giving rise to unrealistic expectations around relationships and intensifying feelings of obsession when they arise. Media portrayals that glorify possessive behaviour further perpetuate this harmful narrative.
- Lack of Boundaries: Inadequate boundaries between partners can pave the way for obsessional dynamics in a relationship. When boundaries are blurred or non-existent, it becomes easier for one partner's infatuation to veer into dangerous territory where possessiveness takes over.

Mental Health Issues: Certain mental health conditions such as borderline personality disorder or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) may contribute heavily towards developing obsessive forms of love due to their illnesses' intrusive thoughts and patterns exhibited by those disorders.
Recognising these contributing factors lays the groundwork for understanding how obsessive love manifests and allows for the implementation of healthier relationship dynamics through increased self-awareness and open communication.
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD)
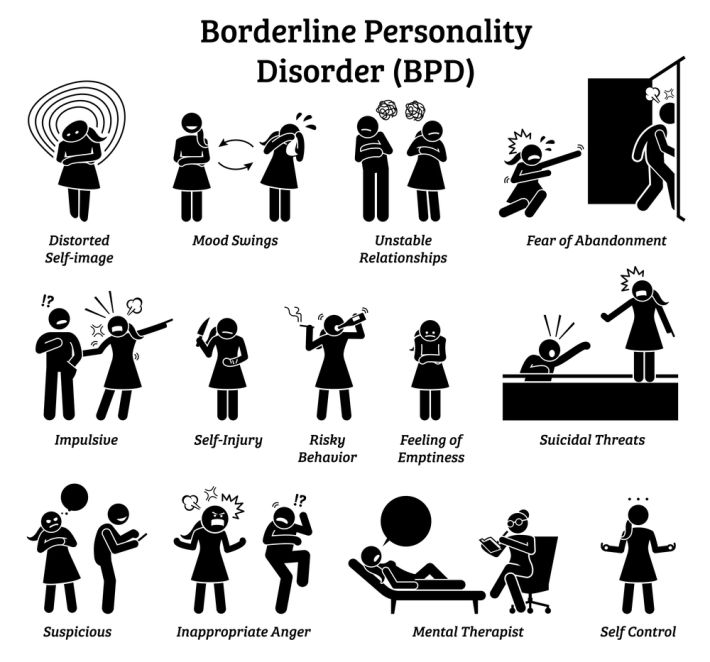
Although not solely focused on love disturbances, individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder often have unstable and intense relationships.
They may constantly fear abandonment, have a distorted self-image, and exhibit impulsive and self-destructive behaviours in romantic relationships.

In this case, Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) being a mental health disorder characterized by recurrent unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviours (compulsions). These obsessions can be intrusive and distressing, causing individuals to engage in compulsions as a way to alleviate anxiety or prevent a feared outcome.
In the context of love, someone with obsessive-compulsive disorder may have intrusive thoughts about their partner cheating on them or may feel compelled to constantly seek reassurance from the partner about their feelings.
Love Addiction:
Similar to other forms of addiction, individuals with love addiction become excessively dependent on the emotional high of being in love. They may constantly seek out new relationships or engage in compulsive sexual behaviours to fulfil their need for love and validation.
It is important to remember that these disorders are severe mental health conditions and should be treated by professionals.
If you or someone you know is struggling with delusional or obsessive love disturbances, seeking help from a therapist or psychiatrist is crucial for managing and overcoming these challenges.
Psychoanalysis is a therapeutic approach that aims to uncover the unconscious motives and desires that drive our behaviours and emotions.
Psychoanalysis also offers a safe space for individuals to process their intense emotions, fantasies, and desires associated with obsessive love. The therapist acts as a guide and helps individuals explore and navigate the complex dynamics at play.
Through this exploration, individuals can develop healthier coping mechanisms, establish healthier boundaries, and build more fulfilling relationships.
It is essential to note that psychoanalysis is a long-term therapeutic approach that involves regular sessions over an extended period.
The depth and intensity of this approach allow for a comprehensive exploration of the roots and manifestations of obsessive love.
A healthy relationship is a mutually beneficial and supportive connection between individuals that is built on trust, respect, and effective communication. It involves open and honest conversations, shared goals and interests, and a commitment to growth and well-being for both parties.




[…] Wilkes, exhibits characteristics of a psychological illness known as obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Annie's intense infatuation and obsession with the character, Paul Sheldon, can be seen as a […]